Zeolite
BROCHURES



Product DESCRIPTION
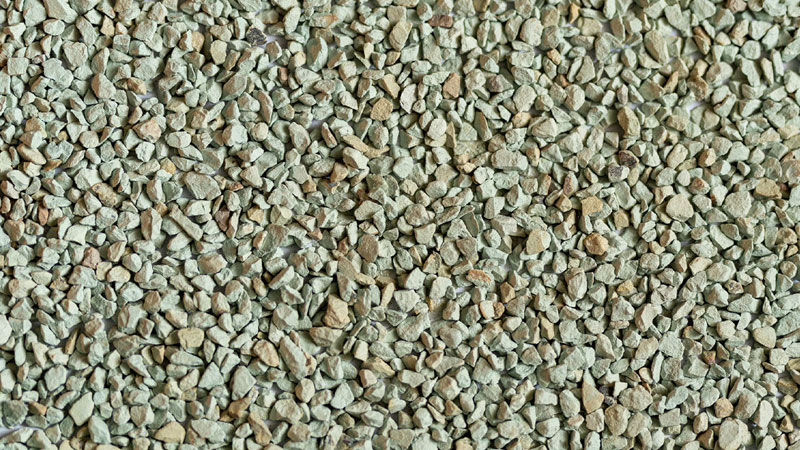
Zeolite is a naturally occurring mineral known for its unique crystalline structure and remarkable adsorption properties. It is formed from volcanic ash and seawater over millions of years, resulting in a porous structure with a high surface area.
This structure allows zeolite to effectively trap and remove various pollutants, contaminants, and impurities from water, soil, and air. Additionally, zeolite can exchange ions with surrounding solutions, making it valuable in various industrial processes such as water softening and purification.
Its versatility and eco-friendly nature make it a popular choice for applications ranging from water treatment and agriculture to gas separation and odor control.
Zeolites are fascinating minerals with a wide range of uses due to their unique properties. Here are some of their main applications:
- Water purification: Zeolites have a porous structure that allows them to effectively adsorb and remove heavy metals, ammonia, and other contaminants from water. They are commonly used in both municipal and industrial water treatment systems.
- Air purification: Similar to their use in water purification, zeolites can also adsorb volatile organic compounds (VOCs), odors, and other pollutants from the air. They are used in air filters for homes, offices, and industrial facilities to improve indoor air quality.
- Detergents: Zeolites are often included in laundry detergents as water softeners. They can exchange calcium and magnesium ions in hard water with sodium ions, preventing the formation of scale and improving the effectiveness of the detergent.
- Catalysis: Zeolites have a crystalline structure with uniform pore sizes, making them excellent catalysts for various chemical reactions. They are used in petroleum refining, petrochemical production, and other industrial processes to speed up reactions and increase yields.
- Gas separation: The molecular sieving properties of zeolites make them useful for separating gases. They can selectively adsorb certain gases while allowing others to pass through, which is valuable in applications such as oxygen production, gas purification, and natural gas processing.
- Nuclear waste remediation: Zeolites can immobilize radioactive ions, making them useful for the cleanup and storage of nuclear waste. They can trap radioactive isotopes within their porous structure, reducing the risk of environmental contamination.
- Animal feed additives: Zeolites are sometimes added to animal feed to improve digestion and absorb toxins in the gastrointestinal tract. This can help prevent diseases and improve the overall health of livestock.
- Construction materials: Due to their high porosity and ability to adsorb moisture, zeolites are used in construction materials such as concrete and plaster to enhance their durability and moisture resistance.
zeolites indeed have several applications in agriculture. Here are some of the key ways in which they are used:
-
Soil Amendment: Zeolites can improve soil structure and fertility. Their porous structure helps to retain water and nutrients in the soil, making them available to plant roots over an extended period. Additionally, they can buffer soil pH, making it more conducive to plant growth.
-
Nutrient Management: Zeolites can act as carriers for fertilizers and micronutrients. They can adsorb and release nutrients slowly over time, reducing nutrient leaching and increasing their availability to plants. This helps in reducing fertilizer runoff, which can be environmentally damaging.
-
Water Retention: Zeolites have a high cation exchange capacity (CEC), allowing them to retain water and nutrients in the soil. This property is particularly beneficial in arid and sandy soils, where water retention is a challenge. By enhancing water retention, zeolites can help plants withstand drought conditions and reduce irrigation needs.
-
Odor Control: In animal husbandry, zeolites are used as stall deodorizers and ammonia absorbers. They can adsorb and neutralize odorous compounds and ammonia in animal waste, improving air quality in barns and reducing the risk of respiratory issues in livestock.
-
Livestock Feed Additive: Zeolites are sometimes added to animal feed as a feed additive. They can bind mycotoxins and other harmful substances in the gastrointestinal tract, reducing the risk of digestive disorders and improving animal health.
-
Pesticide Carrier: Zeolites can be used as carriers for pesticides and herbicides. They can adsorb and release agrochemicals slowly over time, reducing the frequency of applications and minimizing environmental contamination.
-
Seed Coating: Zeolites are used in seed coatings to improve seed germination and plant establishment. They can retain moisture around the seed, provide a protective barrier against pathogens, and deliver nutrients to the emerging seedling.
-
Soil Remediation: Zeolites can help remediate contaminated soils by adsorbing heavy metals and other pollutants. They can immobilize contaminants, reducing their bioavailability and preventing them from leaching into groundwater.
Overall, zeolites play a crucial role in sustainable agriculture by improving soil health, increasing nutrient efficiency, and mitigating environmental impacts. Their versatile properties make them valuable tools for enhancing crop productivity and reducing the ecological footprint of agricultural practices.